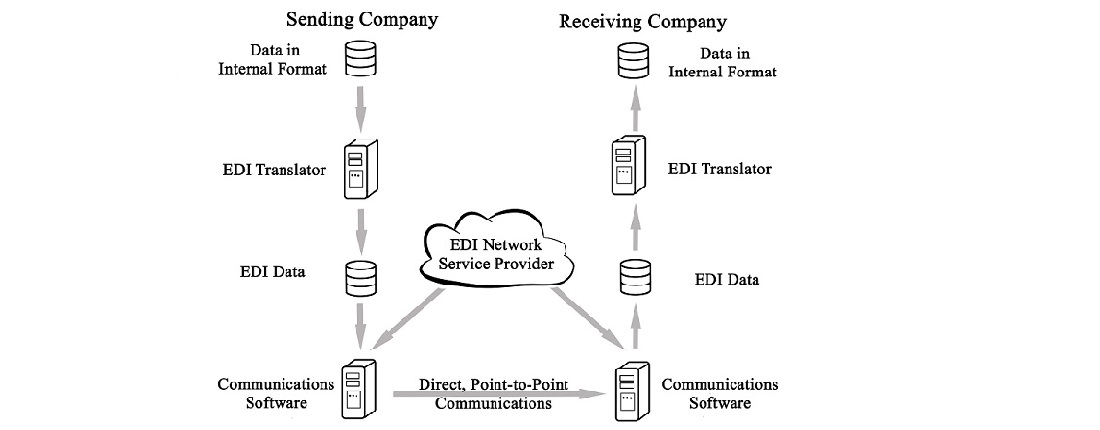
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) communication protocols are a set of standardized rules and conventions that govern the exchange of electronic business documents between different computer systems. These protocols ensure that data is transmitted accurately, securely, and efficiently between trading partners in various industries. Here are some common EDI communication protocols:
API (Application Programming Interface)
An Application Programming Interface, commonly referred to as an API, is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate with each other real-time. It defines the methods and data formats that developers can use to request and exchange information between software systems. APIs and EDI serve the purpose of enabling different business systems to communicate and share data. They are essential for connecting vendors to the retailers they do business with and integrating with various systems. However, the choice between using an API or EDI for integration depends on whether the systems involved offer API support. If they do, an API can be used to establish a new EDI integration, making the process more seamless and efficient.
API serves as a communication method that not only facilitates EDI connections but also provides a broader range of capabilities and flexibility. When EDI integration is built using an API, it allows companies to go beyond the limitations of standard EDI.
AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
AS2, which stands for "Applicability Statement 2," is a widely used protocol for secure and reliable data transmission over the Internet. It is commonly employed for Electronic Data Interchange transactions, allowing businesses to exchange sensitive data, such as purchase orders and invoices, in a secure and standardized manner. AS2 EDI uses MDNs to provide real-time feedback on message delivery and processing status, enhancing visibility into the transmission process. It is part of the EDIINT (Electronic Data Interchange-Internet Integration) standards, which define how EDI data can be securely transmitted over the Internet using various protocols, with AS2 being one of the most popular options.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used for transferring files between computers over a TCP/IP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is widely used for sharing and managing files and is supported by various operating systems and applications. It operates on a client-server model. One computer (the client) initiates a connection to another computer (the server) to request and transfer files. The client sends commands to the server, and the server responds accordingly.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
HyperText Transfer Protocol, commonly known as HTTP, is a fundamental protocol used for communication between a client (typically a web browser) and a web server on the World Wide Web. HTTP governs the way web pages and other resources are requested and transferred over the Internet. It operates on a request-response model. A client sends an HTTP request to a server, specifying an HTTP method (such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that identifies the resource to be retrieved or manipulated. The server processes the request and sends back an HTTP response, which includes status information and, optionally, the requested content.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure)
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the standard HTTP used for secure communication over a computer network, most commonly the internet. HTTPS adds a layer of security by encrypting the data exchanged between a user's web browser and a website's server, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the information being transmitted.
SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a network protocol used for securely transferring files between a client and a server over any reliable data stream. SFTP is designed to provide a high level of security during file transfers, making it a preferred choice for organizations that require secure data exchange. SFTP is often run over the SSH (Secure Shell) protocol, providing a secure communication channel for file transfers. SSH provides additional security features such as strong encryption and public-key authentication. It is an open standard and widely adopted in the industry. Many software applications and server platforms support SFTP for secure file transfer needs.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an EDI Communication Method used to transmit EDI files over the internet via email.
VAN (Value Added Network)
A Value Added Network (VAN) is a third-party service provider that offers enhanced features and services to facilitate EDI and other data communication between businesses. VANs play a crucial role in enabling secure and efficient communication between trading partners, helping businesses exchange electronic documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices.
How to Choose the Right EDI Communication Method?
Choosing the right EDI file communication method is crucial for ensuring efficient and secure data exchange between your business and its trading partners. Several factors need to be considered when making this decision:
- Trading Partner Requirements: Start by understanding the EDI requirements of your trading partners. Different partners may have specific preferences or mandates for the communication method they support (e.g., AS2, SFTP, FTPS, VAN). Ensure that your choice aligns with the protocols they can accommodate.
- Security Level: Security is paramount when transmitting sensitive business data. Evaluate the security features of each communication method. Protocols like AS2, SFTP, and FTPS offer encryption and authentication, providing a secure way to transmit EDI files. Make sure your chosen method aligns with your data security requirements.
- Ease of Implementation: Consider how easily you can implement the chosen method within your existing infrastructure. Some methods may require more extensive setup and configuration, while others may integrate seamlessly with your systems. Assess your technical capabilities and resources available for implementation.
- Compliance and Standards: Ensure that the chosen method complies with EDI standards relevant to your industry. Different industries may have specific standards (e.g., ANSI X12, EDIFACT) that must be followed. Confirm that your communication method can handle these standards appropriately.
- Implementation Cost: Evaluate the cost associated with each communication method. Some methods may have upfront implementation costs, ongoing subscription fees, or usage-based charges. Compare these costs against your budget and the expected ROI of EDI integration.
- Redundancy and Reliability: Look for redundancy and reliability features. Can the chosen method handle failover to ensure continuous operation in case of server or network failures? Reliability is essential to prevent disruptions in your EDI processes.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Assess how well the chosen method integrates with your existing business systems, including your Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. Seamless integration can streamline data flow and reduce manual intervention.
Ultimately, the right EDI file communication method will depend on your specific business needs, trading partner requirements, and technical capabilities. Careful evaluation of these factors will help you make an informed decision that supports your EDI integration goals.
To know more on how we implement EDI and integrate into any of their internal systems, contact our sales department at +1 888-339-0722 or email us at sales@infoconn.com